KRC CNC Routers – High-Performance Woodworking CNC Solutions
KRC CNC routers are engineered to deliver top-tier performance in demanding production environments. As a leading CNC machining center manufacturer, KRC offers the best wood CNC solutions for precision, speed, and durability.
Whether you're operating a nesting CNC router for cabinet production or a fully automated system with automatic loading wood CNC capabilities, KRC machines are designed to boost throughput and minimize downtime. Each wood machining center is built for reliability and integrates seamlessly with tooling setups using a chipload chart for optimal cutting performance.
For businesses focused on quality and speed, KRC delivers the production-efficient CNC router technology needed to stay ahead.
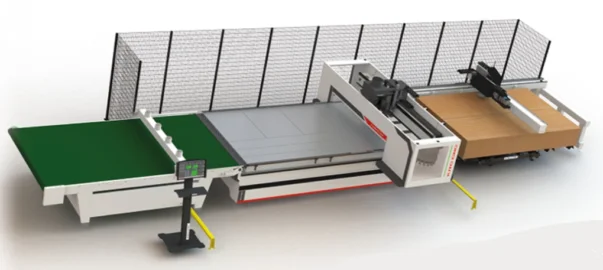
Key features of KRC CNCs offered by Nutek Machinery include
- Powerful Beckhoff controller, servo motors and drives.
- Fast acc/dec allowing for faster linear cutting speeds without excessive tooling wear in corners.
- X and Y axis 90 m/min rapid travel.
- X and Y axis 127 m/min vectorial speed.
- Temperature monitoring of all servo motors.
- Spindle vibration and temperature monitoring for increased spindle life.
- Twenty eight tool change positions.
- Eight vacuum zones with two hundred vacuum points that automatically concentrate vacuum in the area being machined to reduce small part movement.
- Aluminum matrix table.
- Temperature monitoring of electrical panels.
- Heavy frame construction for stability and long machine life.
- Sizes offered 4x8, 5x10, 5x12, 7x10, and 7x12.
Working Area | 5 sizes to choose from |
| Z Axis Clearance | 250mm (with push off device) |
X Axis Motor | 2.3 kW Beckhoff Servo |
| X Axis Rapid Speed | 90m/min |
| Y Axis Motor | 2 x 2.3 kW Beckhoff Servo |
| Y Axis Rapid speed | 90m/min |
| X and Y vectorial speed | 127m/min |
| X and Y acc/dec | 6m/s2 |
| Z Axis Motor | 2.3 kW Beckhoff Servo |
| Z Axis Rapid Speed | 30m/min |
| Spindle Motor Power | 11 kW HSK F63 Hiteco |
| Spindle Rpm | 24000rpm |
| Multi Drill | 9 Vertical (Upgradeable) |
| Control System | Beckhoff |
| Cad Cam Software | Alphacam 2D |
| Lubrication System | Automatic |
| Tool Change | 12 Fixed 16 Rotary Magazine |
| Vacuum Motor Power | 250m3 + 250m3 |
| Vacuum Area | 8 Area Automatic |
| Installed Power | 40 kW |
| Weight | 3800kg - 4200kg |
Selecting the best CNC routing machining center based on processes.
There seems to be an endless number of CNC Routers marketed for the woodworking industry. To ensure you pick the CNC router best for your facility you must first determine how it will be utilized. There are CNC routers that are very application specific. An example would be a CNC router used to produce kitchen cabinet doors, There are also CNC routers and machining centers that are versatile, allowing a multitude of uses.
History of CNC Routers in the woodworking industry.
Decades ago, prior to the advent of nesting, CNC routers were very typically manufactured with one or two moving tables. One of the primary uses for these routers was in the production of cabinet doors. Twin tables allowed the user to load a table with precut panels while the second table was cutting the program. Multiple spindles on the unmoving bridge allowed for multiple doors to be processed simultaneously.
Also popular prior to CNC routing machining centers for nesting were pod and rail machines. Pods referred to the vacuum pods located on moveable rails. Precut panels were placed on the pods raising the bottom of the panel above the rails allowing the parts to be routed on the bottom face of the part. Once again these parts were typically precut with the pod and rail machine drilling, profiling, and carving the parts.
Of course both of these machine types meant parts were handled twice, once during the sizing process on a panel or table saw then again on the fixed bridge or pod and rail CNC. The moving gantry CNC machining center and the process known as nesting changed the woodworking industry forever.
What is nesting on a CNC routing machining center?
Nesting is simply the process of placing a full panel on a CNC table and cutting multiple parts from the panel. Multiple parts arranged on the same panel are said to be nested on the panel. This process meant the parts were only handled once during the sizing and drilling process reducing the number of employees and time spent sizing and drilling individual parts. Improvements in the nesting process like automatic labeling, loading, and unloading increased efficiency and solidified the process of nesting as the most efficient method for small and medium sized facilities to produce parts for cabinetry and closets. Cabinet doors are often nested on a panel, cut, then painted or processed on a thermofoil vacuum press. The same CNC routing machining center can also be used to cut and drill cabinet and closet components resulting in a versatile machine. The versatility works well for shops with limited space and capitol to accomplish numerous processes on one machine but for a large volume door manufacturer the moving gantry nested based cnc routing machining center is much less efficient than a multi-spindle twin table CNC router. It is important to choose the correct CNC for the majority of the product you process when possible to increase production efficiency.
The best nested based CNC routing machining center based on technical specifications and performance
Key features and technical specifications when choosing the best CNC for your facility.
You have determined a nested based CNC routing machining center is the proper choice based on use in your facility. Now is the daunting task of determining which of the many brands is best for you. A great place to start is to understand which features and specifications affect production efficiency and dependability. There are numerous specifications and features to consider but the following are among the most important.
Vacuum zones
If you can’t hold a part firmly while drilling and cutting you can’t achieve accuracy and reduce waste. The vacuum hold-down of panels becomes one of the most important machine specifications when comparing brands. Vacuum should be concentrated to the size of the panel being processed. Panels you will process come in a multitude of sizes. Most common in the U.S. are 4x8, 5x9, 5x10, and 5x12. Consider a single zone 5x12 vacuum table processing a 4x8 panel. The 5x12 table has sixty square feet of surface. A 4x8 panel has thirty two square feet of surface. This results in a single zone 5x12 table having twenty eight square feet of open surface and an incredible amount of vacuum loss through the unused portion of the spoilboard. This vacuum loss results in parts that move during the machining process. If you want to efficiently process multiple panel sizes a minimum number of zones should be equal to the number of panel sizes you process. Having additional vacuum zones above the number of panels you process will help to concentrate the vacuum on cut parts and reduce the loss of vacuum as spoil board is exposed during the machining process. It is also critical to make certain you have the proper number of pumps to maximize the size of the vacuum table.
Rapid travel axis speed
Faster moving axis reduce the amount of time needed to traverse from point A to point B. Saving seconds on travel can add up to a substantial amount of time during the course of a production shift. Incredibly important is the rapid travel time of the Z-axis. A large portion of the machining time when cutting cabinets and closets involves drilling. The Z-axis is slower than the X and Y-axis. Having a faster Z-axis rapid travel will result in reduced cycle times during the machining process.
There are several important factors when determining the maximum cutting speed. A high proportion of CNC routing and machining centers manufacturers have misrepresented the maximum cutting speed of their machines. Parameters for maximum cutting speed can be set even as high as the rapid travel speed but the CNC isn’t always capable of really cutting at those speeds. Important when determining the true maximum cutting speed of a machine are the following:
· Axis acceleration/deceleration speed
· Size of main routing spindle
· Weight and rigidity of the machine
Axis acceleration/deceleration speed
Although manufacturers almost always list the max travel speeds of their machines and often the maximum cutting speed set by the machine parameters they rarely list the acceleration/deceleration speeds of the axis. Why is the acceleration/deceleration speed important? For the actual nesting speed of a CNC routing machining center you have to consider how quickly the machine can get to cutting speed and how quickly it can slow down when doing corners. For every nested piece there are at least four corners that the CNC will have to slow down and accelerate when cutting. Common line cutting can help reduce the number of slow downs but will often result in additional slower Z-axis movements as the cutting tool moves out of the material and back in again. The point to consider when cutting corners is the distance and amount of time the deceleration takes as well as the amount of time the acceleration back to cutting speed takes. The longer it takes to accelerate and decelerate the longer the cycle time for the program will be. It is also important to understand the chipload formulas that result in better cut quality and longer tool life. If a manufacturer has set the linear cutting speed at a high number but the machine has a slow acceleration/deceleration speed the cutting tool will produce a fine dust, resulting in excess heat and reduced tooling life.Size of main routing spindle
The main routing spindle should be large enough to handle the work load when cutting at the maximum linear cutting speed. Spindles that are undersized will bog down during the cutting process.
The main routing spindle is one of the most expensive parts on most CNC routers. Features such as vibration and temperature monitoring can save users from costly repairs that result from overtaxing the spindle or out of balance tooling.
Weight and rigidity of the machine
A heavier built machine is capable of faster cutting, acceleration/deceleration and cutting speeds than a light-weight machine. The optimal weight a machine should be for rapid travel, cutting and acceleration/deceleration speeds are the result of complex engineering formulas. A heavy machine can also reduce potential vibration but in this instance weight is secondary to a well designed base with vibration dampening features.
Is speed really that important if you are cutting fifty panels a day or less?
The saying time is money is true. There are of course machines that can cut forty panels in an eight hour shift and if that is all you need to cut, the lower price tag of these machines may be appealing but consider cutting that same number of panels in two hours instead of eight hours. The extra six hours of labor can be used for other processes such as edgebanding, doweling, or assembly. The faster and more efficiently you cut and drill the more profitable you will be due to increased production efficiency. It makes little sense to spend an eight hour shift doing something that can be accomplished in two hours. The cost of labor and the reallocated labor hours will often more than offset the higher cost of a machine capable of processing more parts when compared to the cost of a slower CNC.
Drill block size and speed
A higher rpm drill block capable of faster feed rates will increase efficiency. Make certain the drill block can hold the number of drills you need to use on a regular basis.
The brand of controller and servo motors
There are numerous controllers on the market with varying degrees of functionality. The KRC CNC routing machining center offered by Nutek Machinery utilizes German made Beckhoff controls. Beckhoff controls offer a high level of functionality, reliability, and ease of use, setting it apart from other controllers.
Number of tool change positions
A higher number of tool change positions offers versatility while eliminating the need to maintain multiple tool sets.The speed of the automatic labeling system if your new nested based cnc routing machining center has one. The automatic labeler is often the bottle neck of a CNC center. Look for an automatic labeler with a ride along printer to reduce axis travel time and reduce the amount of time between placing labels on panels. The labeler is often the bottle neck of the system so make certain the labeler can place a label faster than the machine can cut out a part to optimize the speed of the system. The Phantom by KRC CNC places a label every 4 seconds making it one of the fastest in the industry.
There are numerous other features and specifications that help determine the best cnc routing machining center for your facility but the above features serve as an important place to start in your evaluation.
